Types of Unemployment in Economics
We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us. The level or rate of unemployment is the unemployed share of the labor force in a given country calculated and stated as a percentage.
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help
The price of labor is taken.

. In the months before Christmas sales usually skyrocket. This comprises frictional structural and surplus unemployment. Fixed costs might include the cost of building a factory insurance and legal bills.
Figure 55 The Natural Level of Employment applies the demand and supply model to the labor market. This further leads to inflation. It examines the allocation of scarce resources by individuals businesses and governments.
Disguised unemployment is generally traced in unorganised sectors or the agricultural sectors. A good example is when companies supply goods for Christmas. Positive macroeconomic factors are comprised of events that ultimately stimulate economic stability and expansion within a country or a group of.
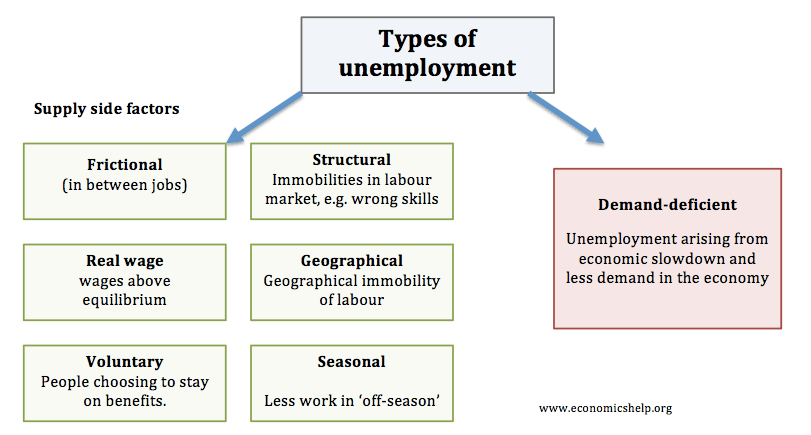
Seasonal unemployment refers to unemployment that is due to seasonal factors. Since both frictional and structural unemployment occur naturally in a market the lowest level of unemployment the US. Types of Managerial Economics.
For instance some businesses make the majority of their sales in only a few months. When the economy is at its peak or experiences continuous growth the rate of cyclical unemployment is low. UNEMPLOYMENT Unemployment refers to a situation in which the workers who are capable of working and willing to work do not get employment.
Fixed Costs FC The costs which dont vary with changing output. It explains why there will always be some level of unemployment even in a healthy economy. Economics is a social science concerned with the production distribution and consumption of goods and services.
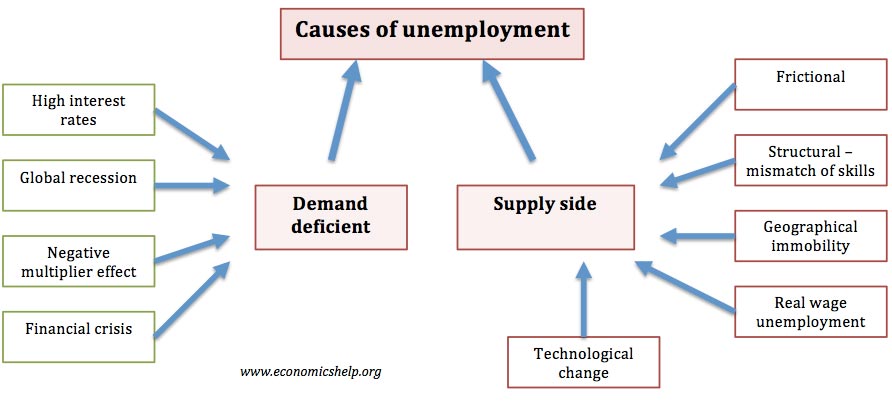
Even if your output changes or you dont produce anything your fixed costs stay the same. Cyclical unemployment is a type of unemployment where labor forces are reduced as a result of business cycles or fluctuations in the economy such as recessions periods of economic decline. Workers may find themselves unemployed for different reasons.
It studies how individuals businesses governments and nations make choices on. Supply-side unemployment the natural rate of unemployment. Demand-side unemployment Unemployment caused by lack of aggregate demand in the economy.
The types of unemployment are discussed below. Everyone has their perceiving ability so the same goes with managerial economics. Natural unemployment consists of two of the three main types of unemployment.
Besides it investigates the reasons behind poverty unemployment and slow economic growth. Government bring-in policies to tackle the problem of unemployment and boost the economy in the short run as well. This unemployment arises when there is a mismatch between the worker.
This is a type of unemployment where people employed are more than actually needed. Each source of unemployment has quite different implications not only for the workers it affects but also for public policy. Micro and macroeconomics are two types of Economics.
These are usually microeconomic imbalances in labour markets. Economics Cafe provides economics lecture notes which are not confined to use by students taking economics tuition at the learning centre. Economy can haveand sustaindepends on how low the rates for these two types of unemployment can go.
Edmund Quek for everyone who can benefit from themThe explanations of economic theories and concepts in the lecture notes are kept concise by design so that they. However after Christmas there are almost no sales at all. All managers perceive the concept of managerial economics differently.
There are main 4 types of Unemployment is which includes. They have been written by the Principal Economics Tutor Mr. Cyclical Frictional Structural 615 Natural Rate of Unemployment.
Understanding market changes and the behavior and performance of an economy can help in resource allocation. People will always be changing jobs and sometimes they leave a job before finding a new one. Definition and Formula 834 Rational Expectations in the Economy and Unemployment 914.
Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of the economy. Because of the cyclical nature of unemployment and based on one of the primary tenets of Keynesian economics about the importance of government interventions the Keynesian theory of unemployment recommends government-driven aggregate demand to reduce unemployment promote consumer confidence and revitalize production during economic. Types of Macroeconomic Factors.
Three Types of Unemployment. Unemployment is a phenomenon that occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable to find work. It is no wonder that unemployment is a top topic of most political debate and that lawmakers often declare that their purposed policies help to create jobs.
Lets study different types of unemployment. Types of unemployment Frictional unemployment Structural unemployment Cyclical or Keynesian unemployment Seasonal unemployment 5. A list and definition of different types of economic costs.
In recessions we can expect demand deficient unemployment sometimes called cyclical unemployment to increase significantly.

8 Types Of Unemployment Understanding Each Type

What Are The Different Types Of Unemployment

No comments for "Types of Unemployment in Economics"
Post a Comment